For Loops
The other main way of looping Python is by using a for loop.
1. Structure of a For Loop
A for loop in python is structured as follows:
for x in <iterable>:
## do something
Both ranges and lists are iterables which means we can loop over them.
1.1 For Loop with a List
A list is a collection of objects. They don't have to be of the same type.
The following 3 examples show a for loop that loops over each item in the list and prints out that item.
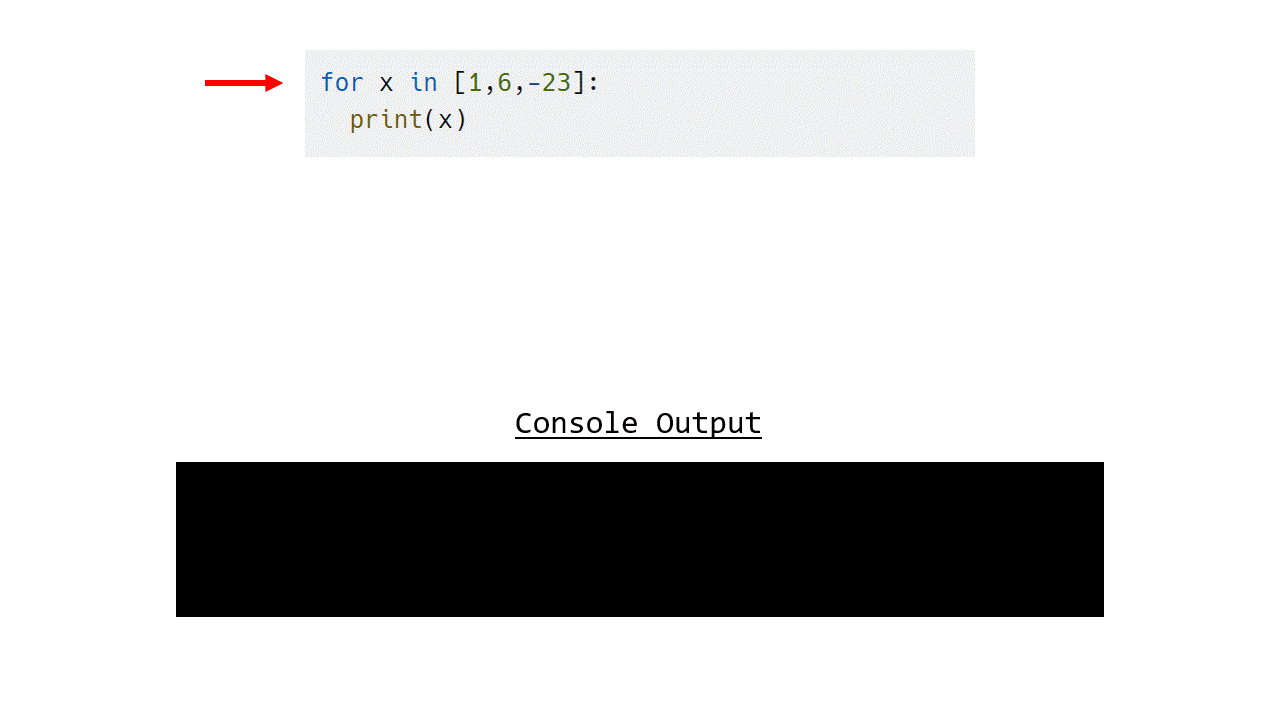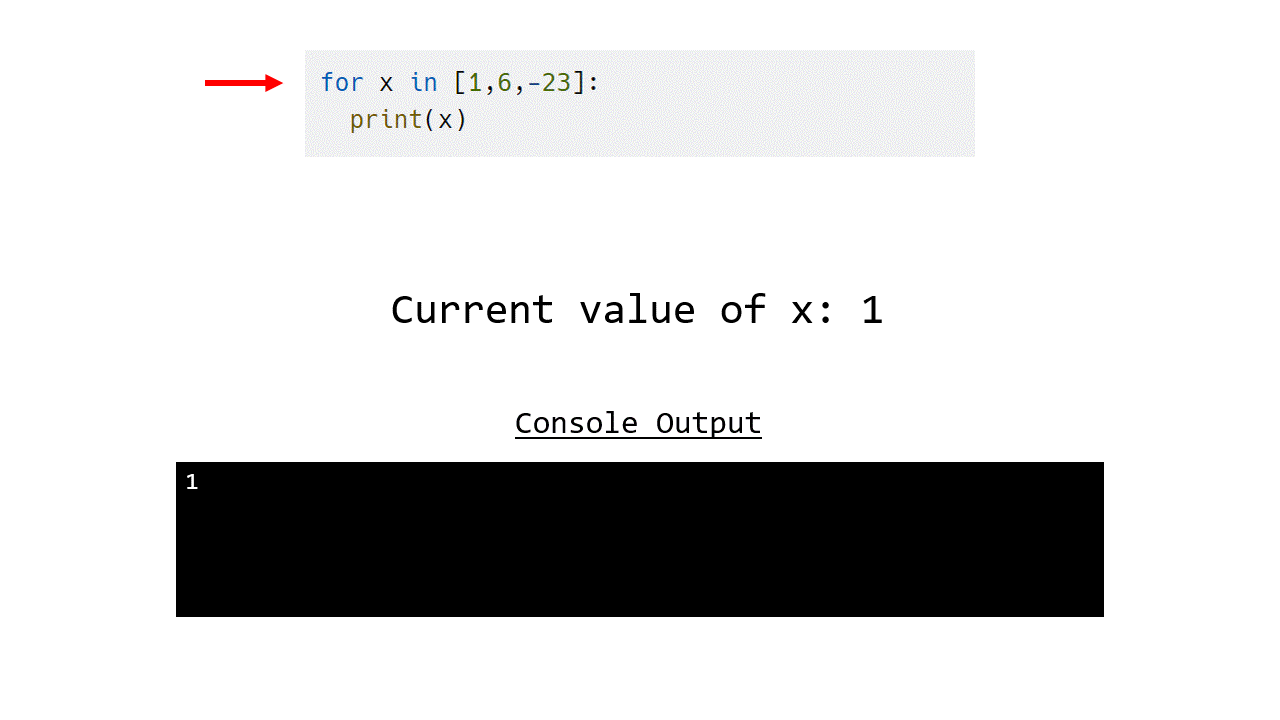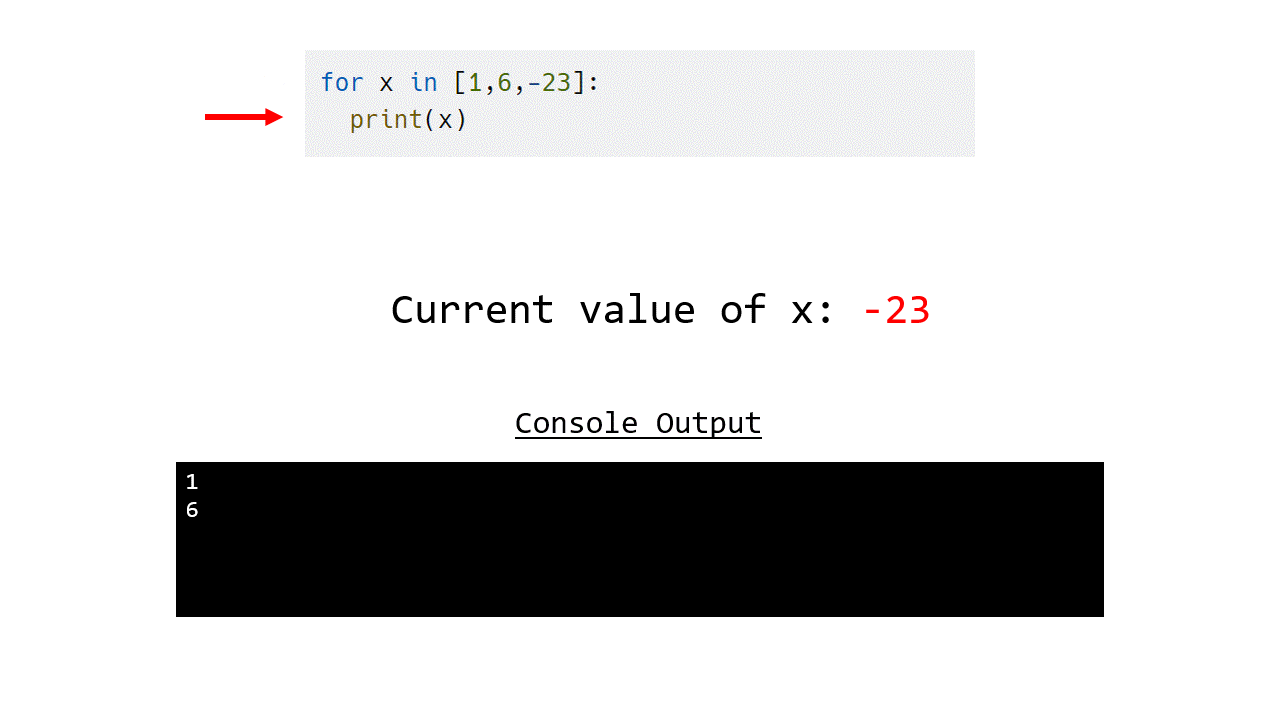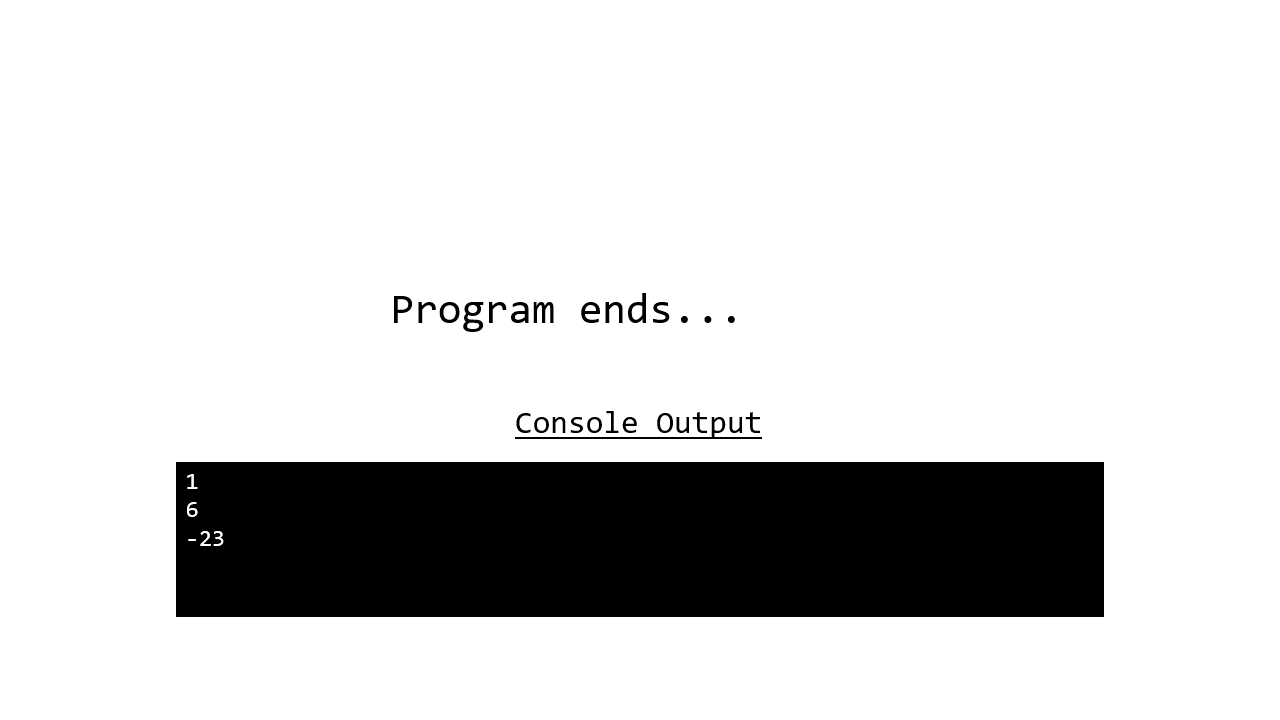
Example 1.1.1 - List of numbers
for x in [1,6,-23]:
print(x)
1
6
-23
The following animation shows how this works.
Example 1.1.2 - List of strings
The following loops over a list of strings,
for x in ["Citreon", "Ford", "Audi", "Mercedes"]:
print(x)
and outputs.
Citreon
Ford
Audi
Mercedes
We can also do this by first assigning the list to a variable and then using this in our for loop.
cars = ["citreon", "ford", "audi", "jaguar"]
for car in cars:
print(car)
Example 1.1.3 - List of different types
The following loops over a list of different types of objects,
for x in ["Citreon", "Ford", 67, True]:
print(x)
and outputs.
Citreon
Ford
67
True
1.2 For Loop with a Range
It is common to use the range() function to automatically generate a sequence of numbers. Do you really want to type out the entire list?
It is also faster and more efficient because it does not have to build the list in memory.
Example 1.2.1
Here range(10) generates the numbers 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9. You can think of it like the list [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9].
The program then prints out double of each item in the list.
for i in range(10):
print(2*i)
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
Example 1.2.2
Here range(3,10) generates the numbers 3,4,5,6,7,8,9. You can think of it like the list [3,4,5,6,7,8,9].
The program then prints out each item in the list.
for i in range(3,10):
print(i)
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Example 1.2.3
Here range(3,20,2) generates numbers using a step size of 2 - 3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17,19. You can think of it like the list [3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17,19].
The program then prints out each item in the list.
for i in range(3,20,2):
print(i)
3
5
7
9
11
13
15
17
19
1.3 For Loop with Underscore
If you are not using the counter variable in the for loop, it is convention to use an _ (underscore).
for _ in range(10):
print("Hello")
The above will print out Hello 10 times.
2. Nested For Loops
Just as we did with while loops, we can nest for loops. Here we use an outer for loop and an inner for loop to print out the multiplication tables.
for i in range(1,13):
for j in range(1,13):
print(f"{i} x {j} = {i*j}")
The animation below demonstrates how this program works, note that instead of printing out the whole table we have limited this to just 1 and 2.
for i in range(1,3):
for j in range(1,3):
print(f"{i} x {j} = {i*j}")
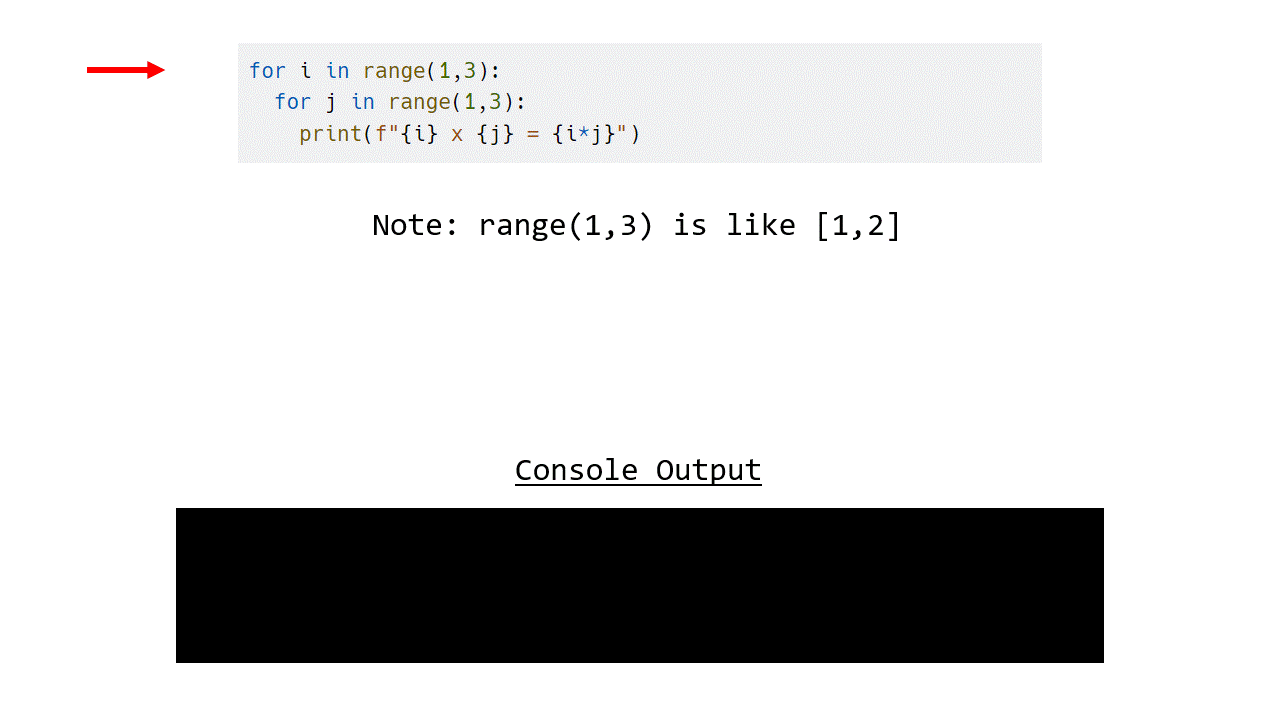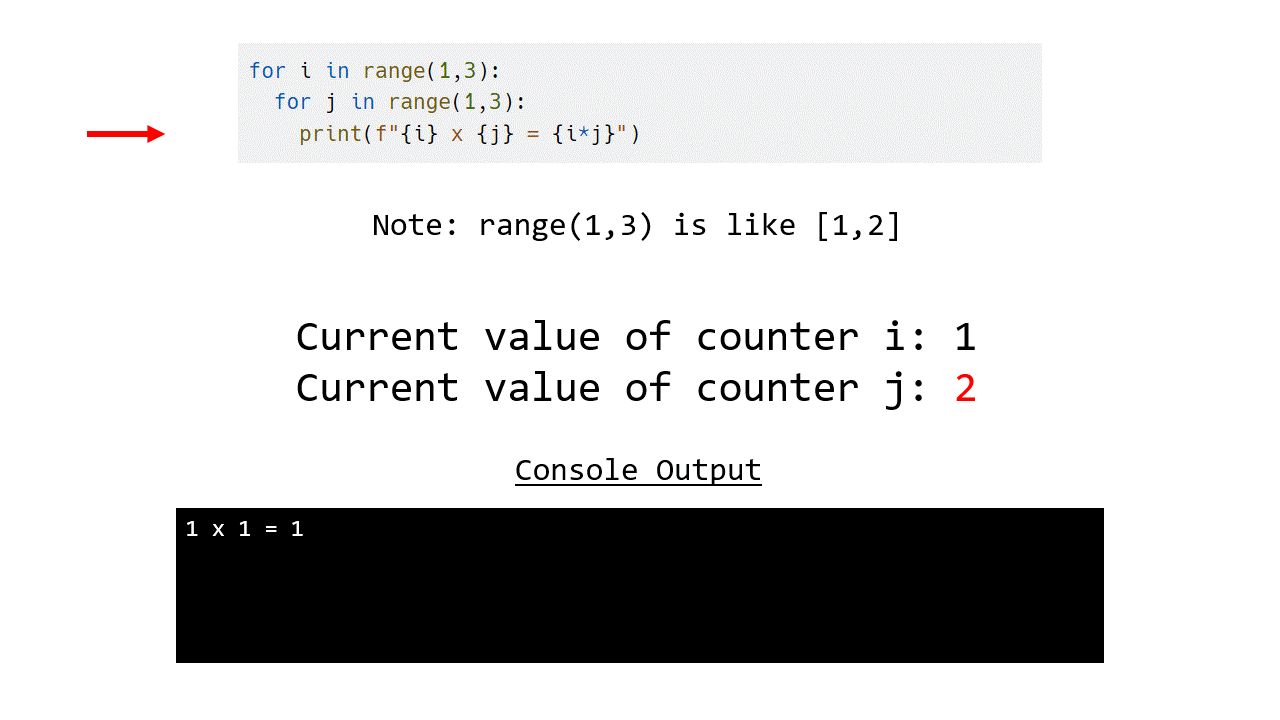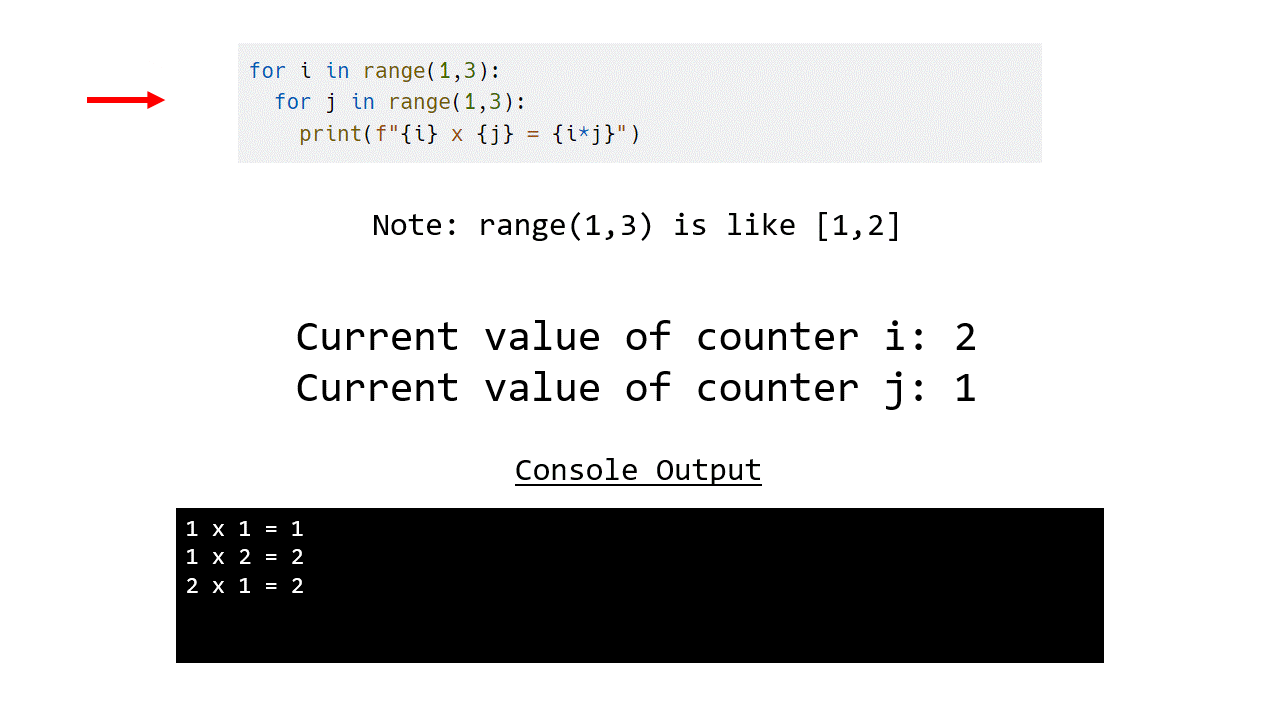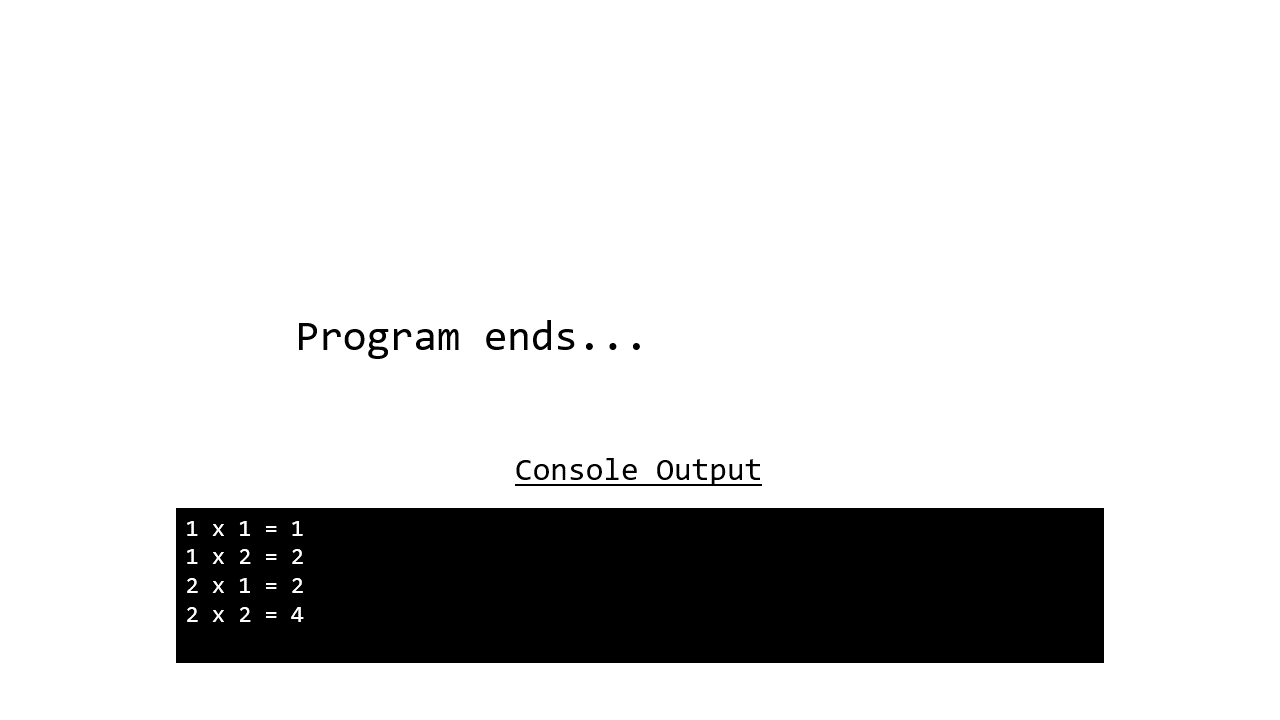
If we compare this to the same program using a while loop, you can see that the for loop version is less verbose and easier to read.
i = 1
while i < 13:
j = 1
while j < 13:
print(f"{i} x {j} = {i*j}")
j += 1
i += 1
=== TASK ===
You can find the length of a string by using the len() function.
For example:
string1 = "for loop"
len_string = len(string1)
print(len_string)
# note you could do this in one line print(len(string1))
This will output the length of the str "for loop". That is, 8.
Copy the following into a new Python file:
# Do not touch this line - It is just there to set up the string list from the input
# string_list will contain a list of strings that have been entered.
string_list = input("Please enter a list of numbers separated by a comma.\ne.g. Citreon,Ford,Audi,Mercedes\n").split(',')
print(string_list)
This code will accept a list of comma-separated strings. e.g. Citreon,Ford,Audi,Mercedes.
If you try running the program and you enter a list of comma-separated strings they will be printed back to the terminal.
['Citreon','Ford','Audi','Mercedes']
The strings inputted are stored in the list named string_list.
Amend the program so that it prints out the following for each inputted string.
The length of the string {string} is {length of string}.
For example, for the string "Ford" the program would print:
The length of the string Ford is 4.
For the input one,two,three,four,five, the whole program acts as follows:
Please enter a list of numbers separated by a comma.
e.g. Citreon,Ford,Audi,Mercedes
one,two,three,four,five
The length of the string one is 3.
The length of the string two is 3.
The length of the string three is 5.
The length of the string four is 4.
The length of the string five is 4.
For the input Citreon,Ford,Audi,Mercedes, the whole program acts as follows:
Please enter a list of numbers separated by a comma.
e.g. Citreon,Ford,Audi,Mercedes
Citreon,Ford,Audi,Mercedes
The length of the string Citreon is 7.
The length of the string Ford is 4.
The length of the string Audi is 4.
The length of the string Mercedes is 8.
Note that to pass the tests you must have exactly the output above, apart from the input which will differ depending on what the user inputs.